GENERAL CHEMISTRY TOPICS
Periodic table
Periodic table of the elements, with element symbols, atomic number, and atomic masses
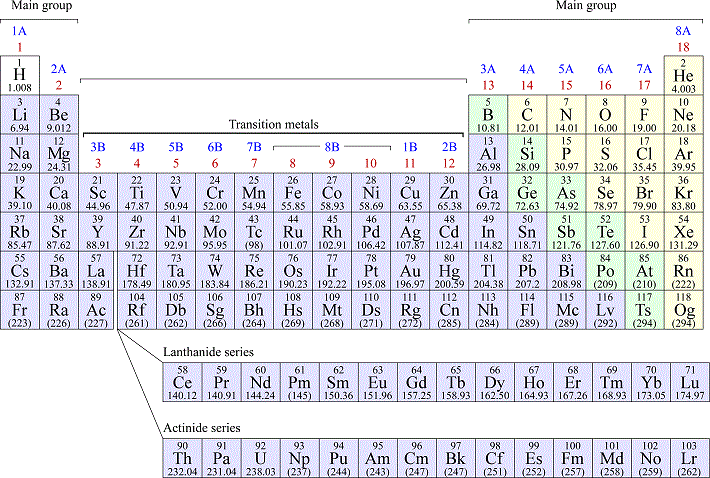
Periodic Table terminology and organization
The color key to the element types, as represented in the table above:
Most elements in the periodic table are classed as metals. The remaining elements are mostly nonmetals, with a small number of semimetals (or metalloids). Terms: Period = row, Group = column. Groups are labeled by two different conventions. Main group elements = the first two groups together with with last six groups. In the first group labeling convention, the main group elements are groups 1A through 8A. The transition metals are made up of a block of 10 groups that are placed in between the main group element groups 2A and 3A. All the transition metal groups are designated by a number followed by the letter B in the first group labeling connvention. The elements in periods are arranged by increasing atomic number Z. The first period consists of only two elements, hydrogen (H) and helium (He). Groups represent families of elements with similar properties. The first group, 1A or 1 (excluding H), are called the alkali metals which are highly reactive metals characteristically participate in forming ionic compounds as +1 charge cations. In the final group, 8A or 18 (including He) are the noble gases, elements that are all very unreactive. The second period consists of the eight elements Z = 3 to Z = 10, beginning with the alkali metal lithium (Li) and ending with the noble gas neon (Ne). The elements of the Period 2 are generally quite common and include what are arguably among the most important elements making up the world around us. Period 3 begins with the next alkali metal, element 11, sodium (Na) and also consists of eight elements, ending with the next noble gas argon (Ar, Z = 18).